Pronouns, at their simplest, are words that replace a name or a noun to avoid repetition when used alongside multiple verbs. They’re a relatively small group of words, but like conjunctions and articles, they’re used all the time. German, like any other language (including English), has different types of pronouns: personal, possessive, reflexive, relative, demonstrative and many more. In this article, we’ll focus on German personal and possessive pronouns.
Personal Pronouns
In German, personal pronouns replace the subject of a sentence. They indicate or represent people or things that are already known to the speaker and listener. You can see the German personal pronouns below.

*es is German’s neuter pronoun.
When these pronouns take on the subject role, the correct grammatical case to use is the nominative. Nominative personal pronouns are one of the most important rules to learn in German, as you need them to produce basic sentences:
- Ich bin Klaus. — I am Klaus.
- Sie kauft ein Auto. — She buys a car.
In these sentences, Ich and Sie are the subjects. Personal pronouns also decline according to their function in the sentence (direct object, indirect object, etc.), as well as when they’re preceded by prepositions that govern a particular case. Below, we can see how personal pronouns decline according to case.
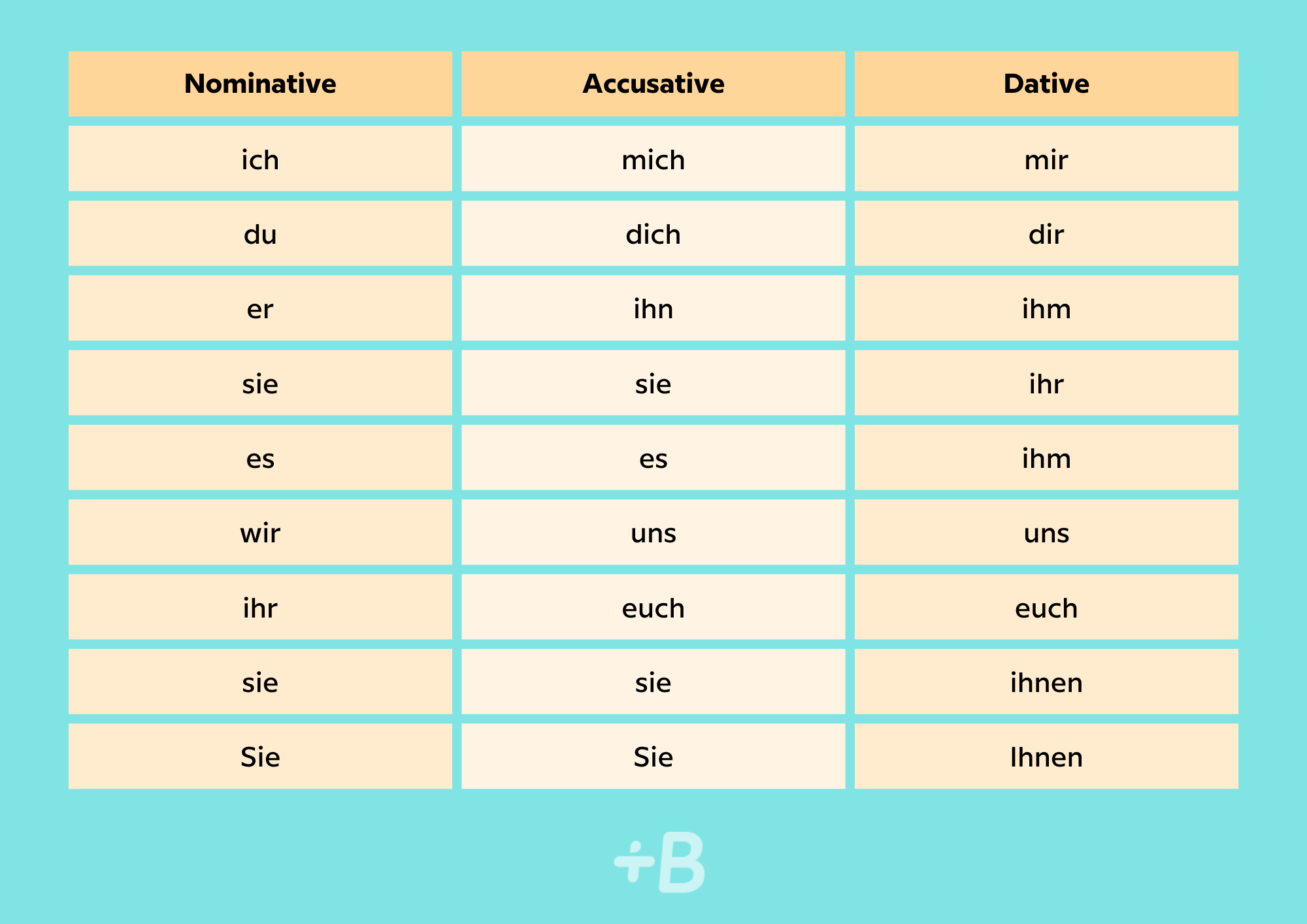
If the pronoun takes on the role of direct object, we use the accusative case, which responds to a “what?” question:
Sie kauft das Auto. → Sie kauft es. — She buys the car. → She buys it.
In this sentence, Sie is the subject and das Auto is the direct object. As das Auto is neuter in gender, we can replace das Auto with the personal pronoun es in the accusative. If the pronoun takes on the role of indirect object, it has to be declined in the dative case. The dative usually responds to a “to whom?” question:
Ich sage Anna. → Ich sage ihr. — I say to Anna. → I say to her.
In this sentence, “Anna” represents the indirect object and is thus replaced by the dative pronoun ihr.
German Possessive Pronouns
Possessive pronouns are words we use to refer to things that belong to us and/or other people. Possessive pronouns replace a noun in the sentence. In English, the words “mine” or “yours” are examples of possessive pronouns. The endings of possessive pronouns also have to agree with the noun to which they refer in gender (masculine, feminine, neuter) and number (singular, plural). Below are the possessive pronouns in the nominative.
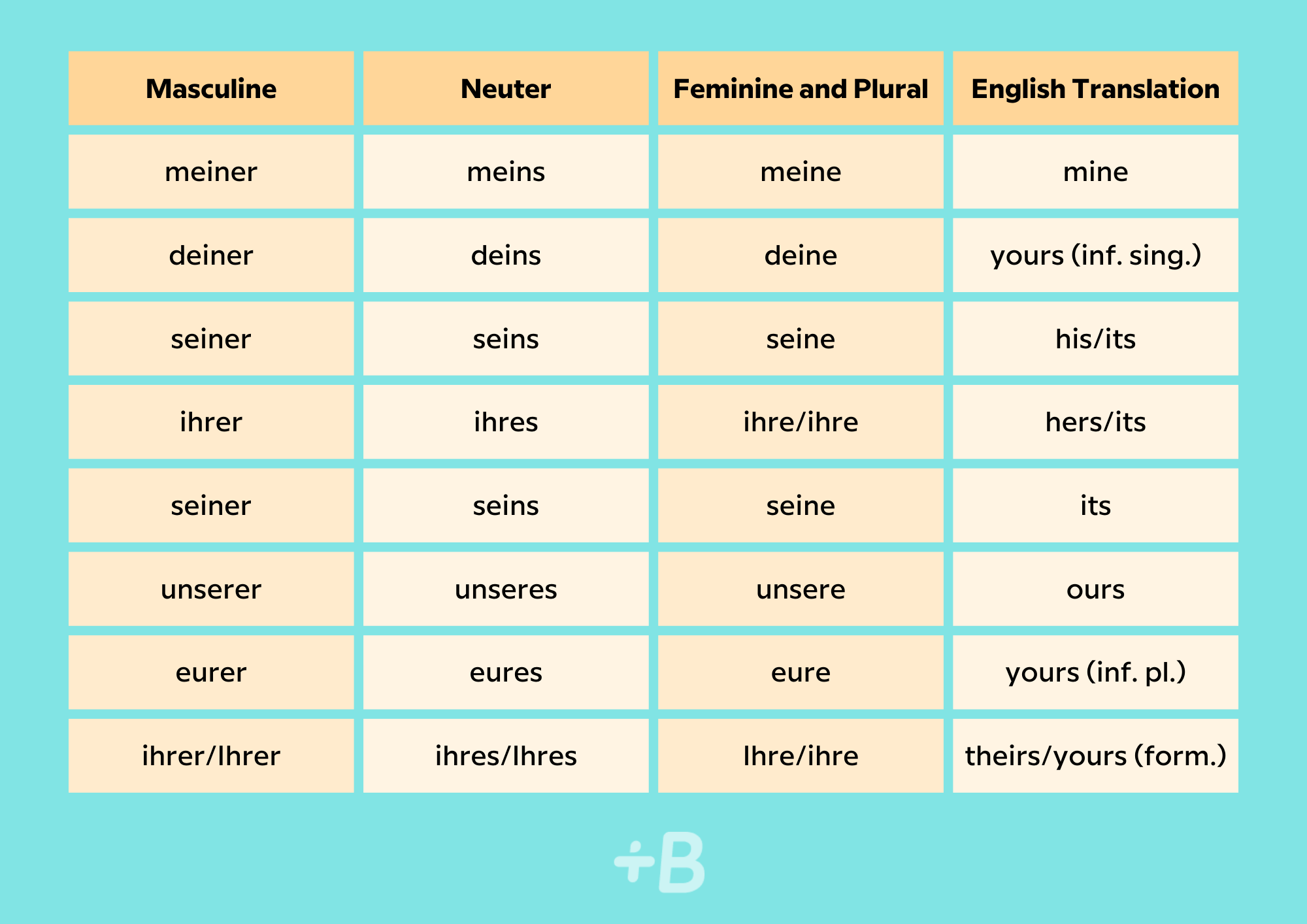
Now let’s take a look at some examples with different gender and number in the nominative case:
- Mein Vater heißt Jonas, und deiner? (“My father’s name is Jonas, and yours?”) — Here, the possessive pronoun “deiner” replaces “Mein Vater”, which is masculine and singular.
- Das ist mein Auto. Das ist meins. (This is my car. This is mine.) — In this sentence, “meins” replaces “mein Auto”, which is neuter and singular.
- Hier gibt es zwei Mützen, sind das eure? (“There are two hats here, are they yours?”) — Zwei Mützen is feminine and plural, so it’s replaced with the possessive pronoun eure.
Just like personal pronouns, possessives decline according to the role of the noun that they replace in the sentence (direct object, indirect object, etc.), as well as when they’re preceded by prepositions that govern a particular case. Let’s have a look at the endings for accusative pronouns.
| Accusative | Ending |
| Masculine nouns | -en (meinen, deinen, seinen…) |
| Neuter nouns | -s or -es (meins, deins, seins…) |
| Feminine and plural nouns | -e (meine, deine, seine…) |
Here’s an example in the accusative case:
Ich kaufe meinen Fahrschein, kaufst du deinen auch? (“I’m buying my ticket (right now), are you buying yours too?”) — The pronoun deinen replaces meinen Fahrschein, which is a masculine noun and performs the function of direct object in the main sentence. Below you can see the endings for dative pronouns.
| Dative | Ending |
| Masculine and neuter nouns | -em (meinem, deinem, seinem…) |
| Feminine nouns | -er (meiner, deiner, seiner…) |
| Plural nouns | -en (meinen, deinen, seinen…) |
Here’s an example in the dative case:
Ich habe meiner Mutter ein Geschenk zum Muttertag gekauft, und du deiner? (“I’ve bought my mother a Mother’s Day gift, have you bought yours one?”) — Deiner replaces meiner Mutter, which performs the function of indirect object in the sentence and is a feminine singular noun.
Coming from English, German pronouns can be a bit difficult, because there are several options where English only has a few. With some practice, however, you’ll get them down, and they’ll come especially in handy when you’re trying to avoid saying those long German words over and over again. Best of luck!
A version of this article was originally published on the Spanish edition of Babbel Magazine.
Comment